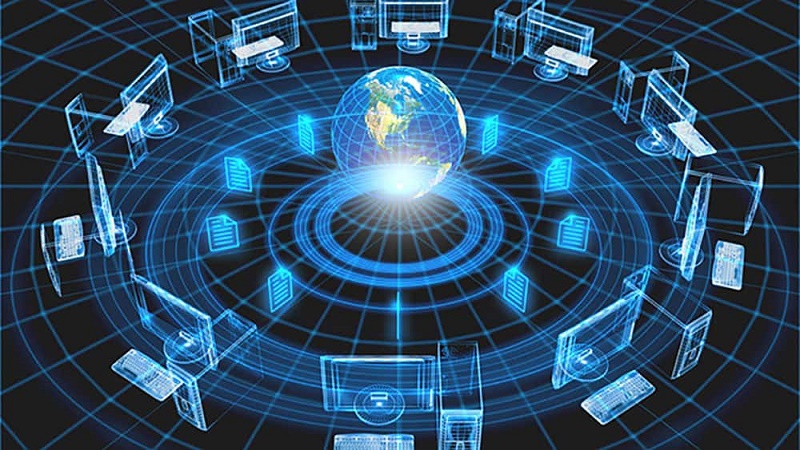
In this digital age, computer networks have become an indispensable part of our daily lives. From the internet that connects us to the vast online world to the local area networks that facilitate communication within organizations, computer networks are the backbone of modern technology. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of computer networks, exploring their definition, components, and various types.
What is a Computer Network?
At its core, a computer network is a group of interconnected computers that share resources and information with each other. These networks can be established through wired or wireless connections, allowing seamless communication and data exchange. The primary purpose of a computer network is to enable the efficient sharing of resources, such as files, documents, printers, and internet connectivity.
The Components of a Computer Network
A typical computer network consists of several key components that work together to ensure its smooth functioning:
- Network Nodes: These are the individual computers or devices connected to the network. Each node has a unique identifier and can both send and receive data.
- Network Links: The connections between the network nodes are known as network links. These links can be wired, like Ethernet cables, or wireless, like Wi-Fi signals.
- Network Protocols: To facilitate communication between devices, computer networks rely on communication protocols. These protocols define the rules and conventions for data transmission.
- Network Switches and Routers: These are essential networking devices responsible for directing data packets between different nodes and networks.
- Network Firewall: A network firewall is a security measure that protects the network from unauthorized access and potential cyber threats.
- Network Server: Servers are powerful computers that store and manage shared resources, providing them to other devices on the network upon request.
Types of Computer Networks
Computer networks come in various shapes and sizes, each designed to cater to specific needs. Let’s explore some of the common types of computer networks:
- Local Area Network (LAN): LANs are confined to a limited geographical area, such as a home, office building, or campus. They facilitate fast and reliable communication between devices within the network.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): WANs cover larger areas, often spanning cities, states, or even countries. The internet itself is the most extensive WAN, connecting users from all over the globe.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): MANs fall between LANs and WANs in terms of size. They cover a metropolitan area, like a city, and are used to connect multiple LANs.
- Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN): WLANs use wireless connections, allowing devices to connect to the network without physical cables. Wi-Fi technology is a common example of a WLAN.
- Client-Server Network: In a client-server network, clients (devices like computers and smartphones) request resources from servers (powerful computers), which then provide the requested resources.
- Peer-to-Peer Network (P2P): P2P networks allow devices to communicate directly with each other without the need for a central server. This type of network is commonly used for file-sharing purposes.
Advantages of Computer Networks
Computer networks offer numerous benefits that have transformed the way we live and work:
- Resource Sharing: Networks allow multiple users to share hardware, software, and data, optimizing resource utilization and reducing costs.
- Communication: Networks enable seamless and instant communication between individuals and teams, fostering collaboration and productivity.
- Information Access: With networked systems, accessing information and data from any connected device has become quick and convenient.
- Flexibility: Wireless networks provide the flexibility to connect devices from anywhere within the network’s range.
- Centralized Management: Server-based networks make it easier to manage and maintain resources, ensuring data security and regular backups.
Challenges in Computer Networking
While computer networks bring tremendous advantages, they also pose certain challenges:
- Security Risks: Networks are susceptible to security breaches and unauthorized access, making robust security measures vital.
- Network Congestion: Increased network usage can lead to congestion and reduced data transfer speeds.
- Hardware Failures: Malfunctioning hardware can disrupt the entire network and affect productivity.
- Compatibility Issues: Different devices and systems may have compatibility issues when connecting to a network.
- Costs: Establishing and maintaining a computer network can involve significant costs, especially for larger setups.
The Future of Computer Networks
As technology continues to advance, so does the evolution of computer networks. Some exciting developments shaping the future of computer networks include:
- 5G Technology: The widespread adoption of 5G technology promises faster and more reliable wireless connections, revolutionizing mobile networking.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The integration of IoT devices into networks will lead to smarter and more interconnected systems, impacting various industries.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing brings computing power closer to the source of data, reducing latency and improving network efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Networking: AI-driven networking solutions will optimize network performance, predict failures, and enhance security.

Conclusion
Computer networks have undeniably become the backbone of our interconnected world. From small local networks to the vast expanse of the internet, they have transformed the way we communicate, work, and access information. Understanding the components, types, advantages, and challenges of computer networks is crucial as we navigate the digital landscape and look forward to the exciting advancements that the future holds.